MICRO-PADDER
Conveyor
Controls, strategically mounted within the cabin, empower operators with comprehensive oversight over material placement, readily accessible at their fingertips. The conveyor system boasts a tri-modal speed selection and a bi-directional capability, facilitating material discharge from either flank of the machinery. Additionally, the conveyor's lateral shifting feature affords enhanced precision in material positioning.
Our distinct tri-segmented conveyor architecture permits each extremity of the conveyor to achieve an inclination of up to 10 degrees during standard operations. This design element amplifies the material's trajectory distance. Upon project culmination, these segments can be elevated to a 90-degree angle, thereby optimizing the unit's transportation profile and consequentially mitigating logistical expenditures.
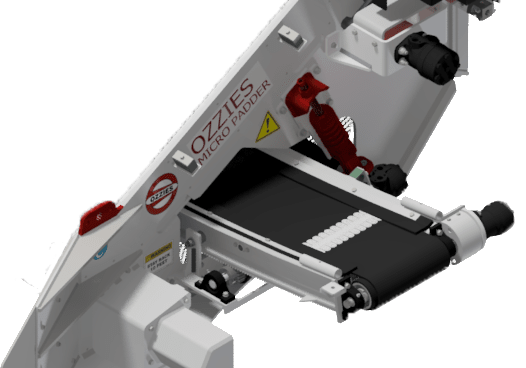
Elevator
Through intensive engineering and thorough testing, we can confidently affirm that Ozzie's Micro-padder screens material in strict alignment with the specified dimensions. Our proprietary adjustable elevator drive system ensures uninterrupted chain engagement, minimizing potential screen rotation discrepancies and ensuring consistent, reliable material processing. Integrated flights adeptly transport oversized material over the screening chain.
The elevator system is managed through a joystick equipped with auxiliary buttons, seamlessly integrated into your standard loader. This elevator boasts bidirectional operation for swift resolution of material blockages and offers three pre-configured speeds.

Compatible loader specifications
Micro-PAdder Specifications
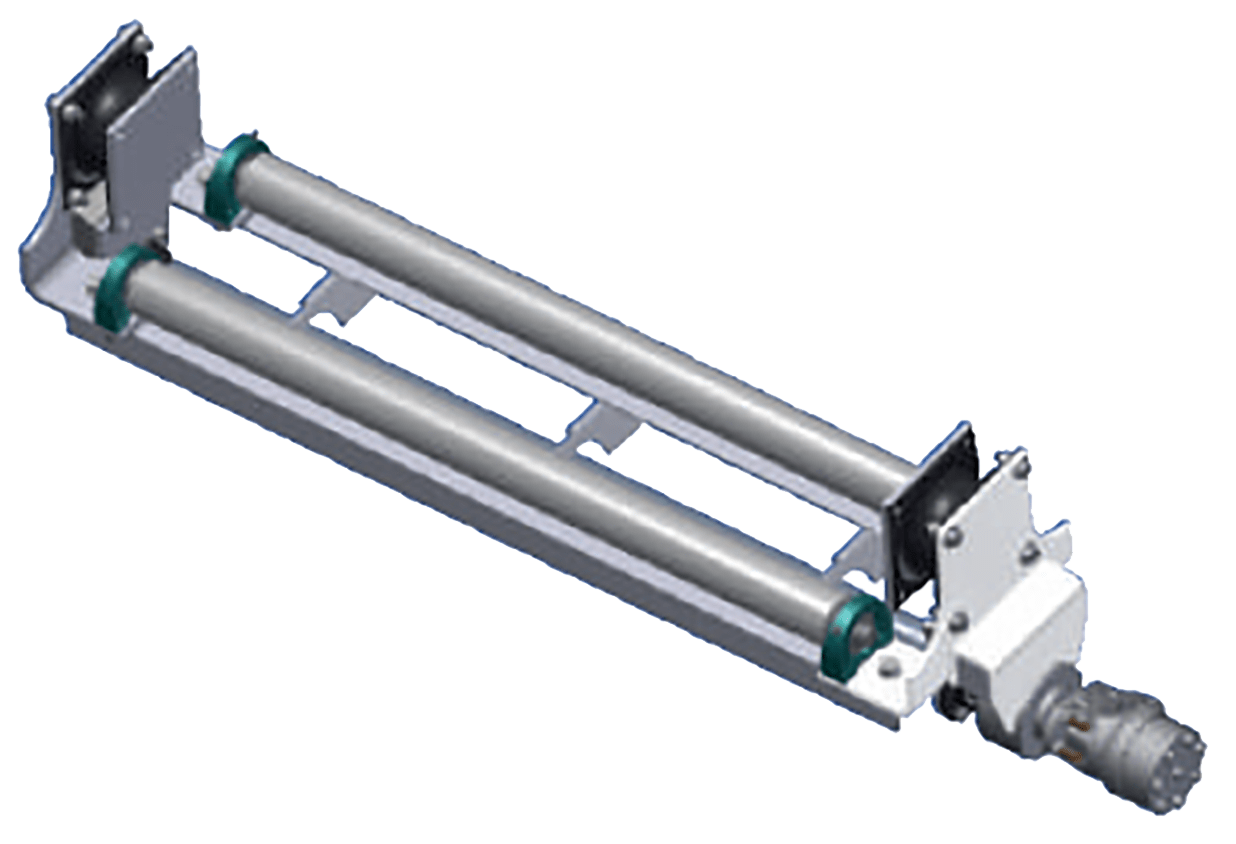
Design: Dual rollers mounted on a framer with an eccentric shaft and hydraulic motor provide agitation of the screen to assist with material processing.
Controls: The vibrator is tuned to a single optimal speed in one direction and is constantly on while the elevator system is activated.
Features: The dual roller system provides screen agitation as well as support to ensure the chain runs true and that oversized material is kept separate from the processed material.
Max Rated Speed: 800 RPM.
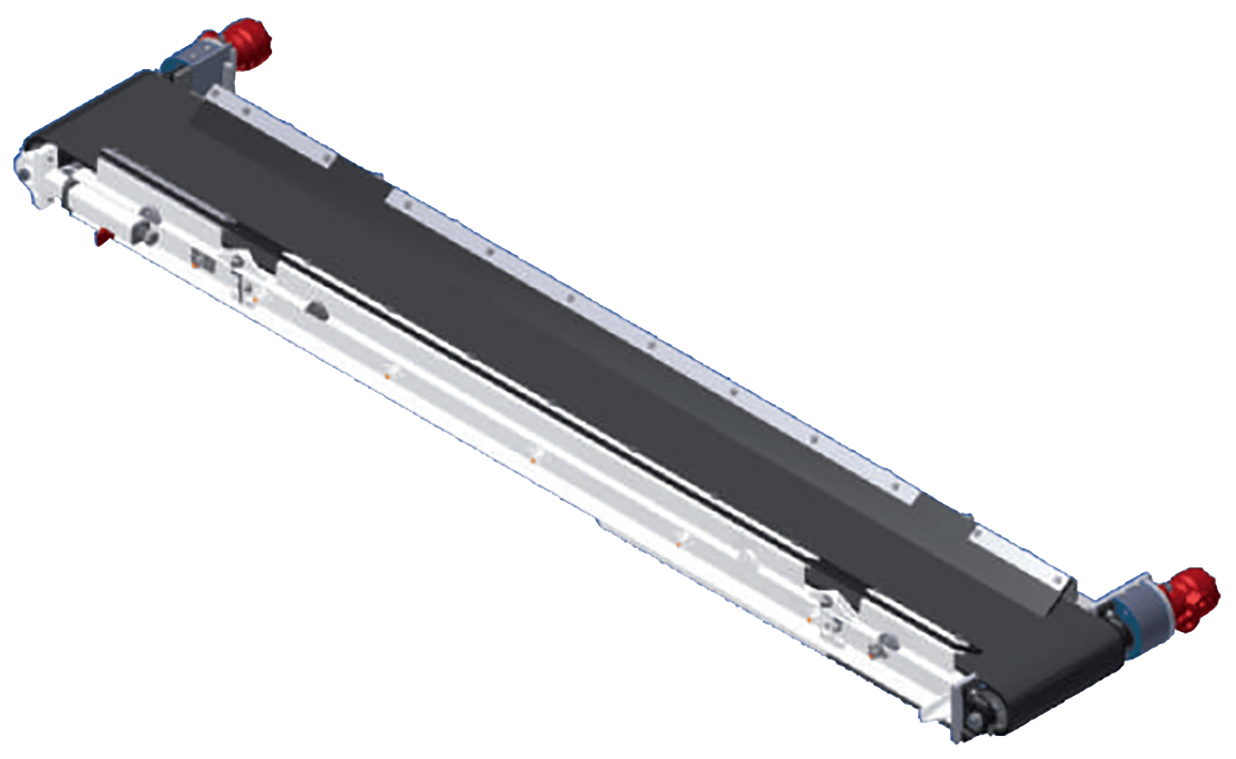
Design: A perpendicular bi-directional conveyor deposits screened material from the elevator into the trench.
Controls: Joystick auxiliary buttons. Three preset conveyor speeds are available in both lateral (left and right) directions.
Conveyor belt: A two-ply 12-inch wide v-groove belt with friction drive backing.
Features: The three-piece design allows for minimum transport dimensions, greater material throwing distance, and lateral shifting. The dual-motor system ensures maximum torque and speed while mechanical adjustors tension the belt to ensure optimal power transfer.
Rated shaft speed: 800 RPM.
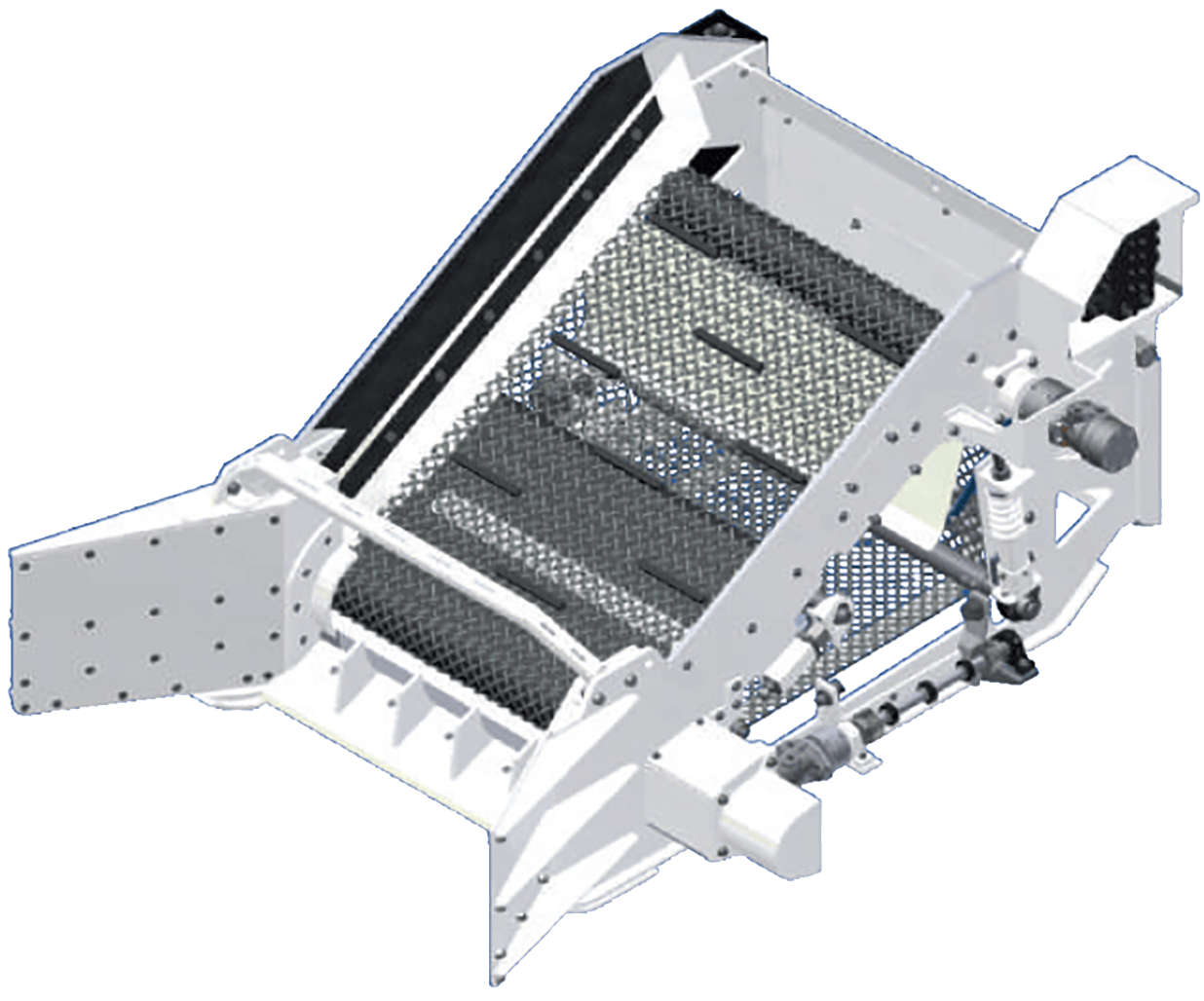
Design: Self-loading, variable speed, continuous screening belt. Screened material is then transferred to the discharge conveyor.
Controls: Joystick auxiliary buttons. In elevator adjustment mode, three forward speeds and one reverse speed setting are available.
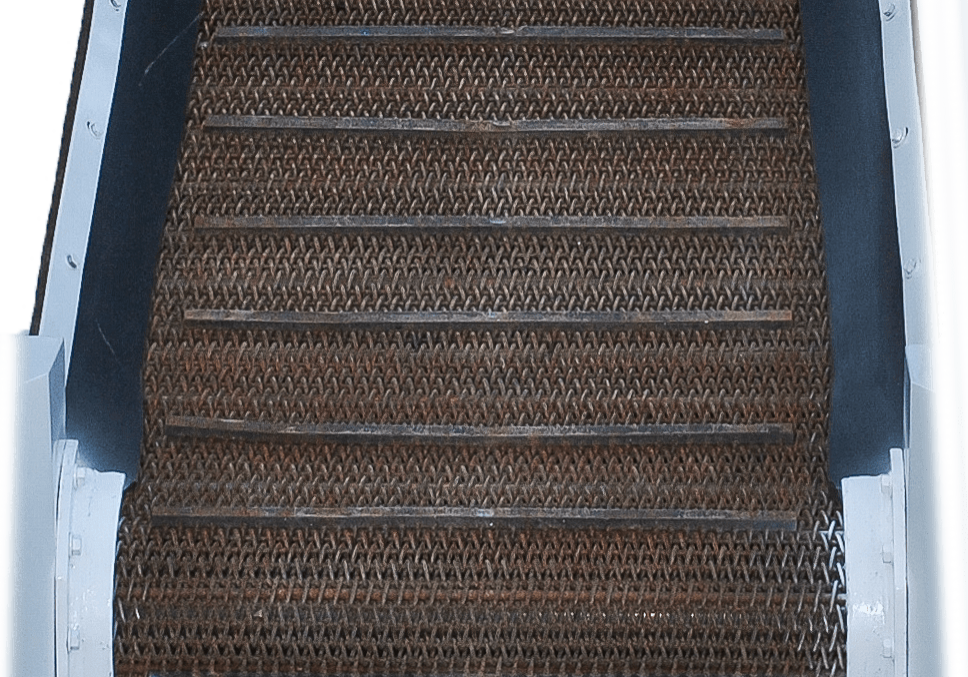
Screen: Interchangeable screen available in 3/8", 5/8", and 7/8" minus producing sizes. A total screening area of approximately 12.75 square feet.
Elevator belt: A two-ply 40" wide v-groove belt with friction drive backing.
Features: Dual Independent mechanical adjustors act as both tensioners and shock absorbers for the elevator screen. Screen cleaning, material clogging, and jamming are quickly completed using the reverse direction setting.
Rated shaft speed: 300 RPM.
Padder Dimensions
Machine Dimensions
Main Applications
The Micro-Padder boasts approximately two-thirds of the processing capacity attributed to the Mini-Padder. Specifically, the Micro-Padder is proficient in processing up to 80 cubic yards (equivalent to 61 cubic meters) of material per hour.
Transport to different job sites and increase operational efficiency by reducing the need for material transportation and processing at a central facility.
Backfill separation is essential in utility projects, contributing to the reliability, safety, and cost-effectiveness of utility infrastructure development and maintenance. It facilitates proper installation and maintenance, minimizes the risk of damage, supports erosion control, ensures environmental compliance, and enhances overall project efficiency.
Backfill separation is a critical practice in telecom projects, contributing to the reliability, safety, and cost-effectiveness of underground telecommunication infrastructure installation and maintenance. It supports proper installation and maintenance, minimizes cable damage risks, aids in erosion control, ensures environmental compliance, and enhances overall project efficiency.
