Direct Benefits
- Reduces damage to the pipeline coating and pipe from rocks and rugged materials that may be situated in the spoil pile;
- Ensures better and more consistent compaction during the backfill process, which contributes to preserving the integrity of the pipeline by securing it in place;
- Facilitates maximum ditch spoil replacement and soil compaction during the backfill process;
- Eliminates soil contamination, what comes out of the ditch goes straight back in during the backfill process – the Green alternative; and
- For underground electrical cables, mechanical padding reduces cable damage from rocks and hard material in the spoil pile and facilitates even heat dispersal through consistent soil compaction.
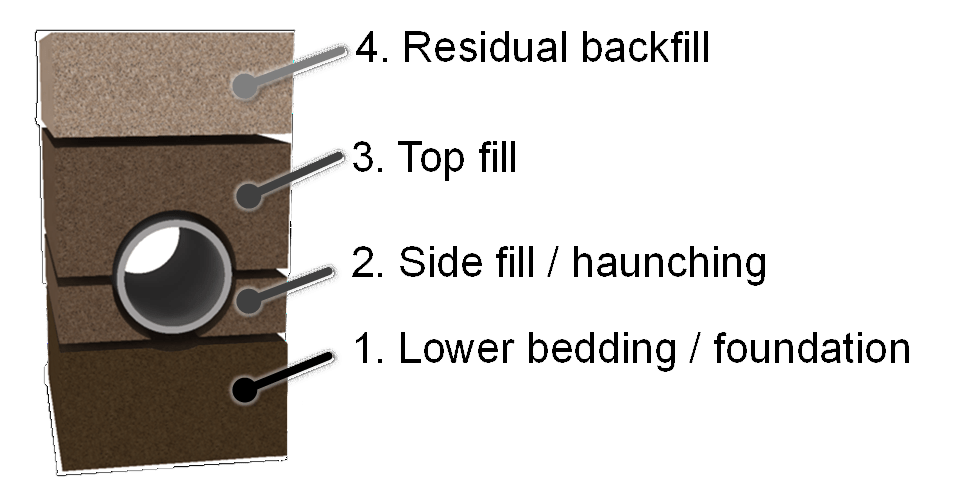
Better Pipe Support
- A pipe that is surrounded by high quality compacted material will support loads and better resist deflection; and
- The shorter the time frame during which the ditch is open, the less likely the possibility of:
- Pipe shifting out of line due to cave-ins;
- External damage (e.g., falling debris, natural causes);
- Pipe lifting due to flooding; and
- Backfill material becoming frozen in cold weather.
BARGAIN PRICE INSURANCE
- Mechanical padding is not just a specialty item for backfilling pipelines where there are known deposits of rock and hard material;
- Mechanical padding is the optimal method of backfilling a pipeline ditch; and
- Proper use of mechanical padding can virtually eliminate any risk of damage to the pipe coating or pipe during the backfill process.
Backfill Considerations
- Availability of backfill;
- Cost of backfill;
- Quality of backfill material;
- Terrain;
- Environmental conditions;
- Project specifications; and
- Productivity/time constraints.
Summary
Ozzies, Inc. provides advanced solutions for backfill separation and renewable energy projects, offering numerous direct benefits. These solutions minimize pipeline coating and pipe damage from rocks and rugged materials, ensure consistent compaction to preserve pipeline integrity, facilitate maximum ditch spoil replacement, and eliminate soil contamination, making it a Green alternative. For underground electrical cables, mechanical padding reduces damage and promotes even heat dispersal. High-quality compacted material supports loads and resists deflection, reducing risks like pipe shifting, external damage, pipe lifting, and frozen backfill material. Mechanical padding is the optimal backfilling method, virtually eliminating damage risks to pipe coatings or pipes. Key considerations for backfill include availability, cost, material quality, terrain, environmental conditions, project specifications, and productivity/time constraints, ensuring efficient and reliable project execution.
